Table of Contents
Selecting the correct powder coating for a specific end-use application is critical but can be a mystery to applicators, product developers, and end users due to the variety of chemistries and industry terminology. To be clear, the best way to ensure you are using the right powder is to thoroughly understand the application requirements and consult with your supplier.
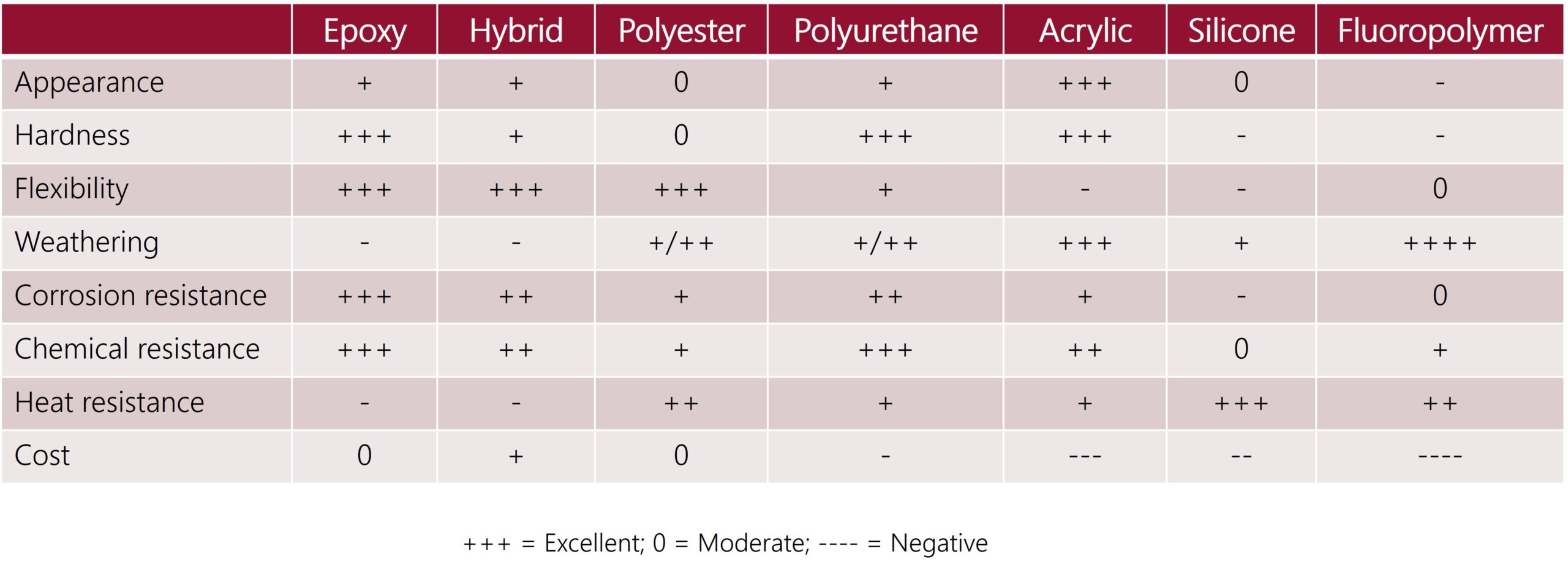
That said, gaining a fundamental understanding of why certain powder coatings are used for specific applications can help you make more informed decisions. This article serves as a high-level guide to the general classes of powder coatings, as well as the performance properties that influence their selection for use in different broad end-use categories (see Table 1).
Before diving into specific applications, two important points must be addressed:
- Powder coatings are typically classified by their main resin chemistry, so a basic discussion of chemistry is necessary for each section. However, this article will keep explanations at a high level.
- Although each type of powder coating has general performance characteristics, properties can vary significantly within each category. This is why it is crucial to discuss your specific end-use application with your supplier to ensure the best choice is made.
With these points in mind, let’s explore how different powder coatings are selected based on application requirements.
Interior Applications
Appliances, Metal Furniture, and Home Goods
Interior applications refer to finished products that will not be exposed to outdoor conditions. While this may seem straightforward, it’s important to distinguish between applications that will be used outdoors but shielded from sunlight and those that are strictly interior and won’t require a high level of corrosion resistance.
For interior applications, hybrid powder coatings are the dominant choice. These coatings are typically based on acid-functional polyesters crosslinked with bisphenol-A epoxies. In cases where higher hardness or chemical resistance is needed, acid-functional acrylics may be used instead of polyester.
In terms of performance, hybrid powder coatings provide sufficient corrosion and UV resistance for indoor applications and can be formulated in a wide variety of colors, sheens, and textures. These coatings also offer a high level of chemical resistance to protect appliances from cleaning agents like bleach, and they exhibit excellent hardness and scratch/mar resistance for applications such as metal office furniture. In addition, they are cost effective and well-balanced in terms of performance.
Functional Applications
Pipelines, Rebar, and Automotive Underbody
Functional powder coatings refer to applications where UV exposure is minimal, but a high level of corrosion, chemical resistance, or some other “function” is required. These coatings must withstand harsh environments such as chemical exposure, moisture, and abrasion, but they do not require UV resistance.
For these demanding applications, epoxy-based powder coatings are the preferred choice. While epoxies cannot be used in direct sunlight due to their poor UV resistance, they offer unmatched levels of corrosion and chemical resistance, as well as excellent mechanical properties such as impact resistance, ductility, and hardness. Common epoxy powder coating types include:
- Bisphenol-A epoxies—the most common epoxy resin; offer excellent adhesion, corrosion protection, and chemical resistance
- Novolac epoxies—provide higher crosslink density for increased chemical resistance; ideal for extremely aggressive environments
Exterior Applications
Architectural Profiles, Lawn and Garden Equipment, Automotive Trim, and Bicycle Frames
Exterior applications require powder coatings with varying levels of UV durability, depending on the product’s exposure to sunlight and weather conditions. While UV resistance is not the only property required for exterior coatings, it is typically the first “filter” used to narrow down to the type (chemistry) of powder coating that should be used in a given end-use application. The three main types of powder coatings used in exterior applications are standard-durable polyesters, super-durable polyesters, and fluoropolymers (FEVEs).
Standard-Durable Polyesters
Typically providing 1-3 years of UV durability, these powder coatings are based on acid-functional polyesters that are crosslinked with either triglycidyl isocyanurate (TGIC) or hydroxy alkyl amide (HAA; also known as TGIC-free). Common uses include lawn and garden equipment, as well as general outdoor metal furniture.
Super-Durable Polyesters
Though similar to standard-durable polyesters, super-durable polyesters are based on polyester resins that are composed of more UV-resistant monomers for improved longevity. They generally provide 3-7 years of UV durability in more rigorous applications such as automotive trim and architectural coatings.
Fluoropolymer (FEVE) Powder Coatings
FEVE powder coatings are based on fluoroethylene vinyl ether (FEVE) resins, crosslinked with blocked isocyanates to create a highly UV-resistant network. These products offer 10+ years of outdoor durability, making them ideal for high-performance architectural coatings and long-lasting exterior applications.
Generally speaking, polyesters provide a good balance of cost and performance for moderate outdoor exposure, while fluoropolymers deliver the highest level of UV resistance and weatherability (though at a higher cost). While the exterior-grade coatings mentioned here perform well for corrosion resistance, an epoxy primer may be recommended to increase corrosion resistance for coatings that will be used in extremely harsh environments.
Less Commonly Used Powder Coating Types
While this article focuses on the most widely used powder coatings for broad end-use categories, powder coatings also offer significant advantages in several specialized applications:
- High-heat applications—Silicone-based powder coatings are extensively used for applications like barbecue grills due to their superior heat resistance.
- Clear, high-clarity coatings—Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) acrylic powder coatings are commonly used for wheel coatings, cabinet hardware, and other applications requiring smooth, transparent films with excellent clarity.
- Anti-graffiti applications—Urethane powder coatings are often used for their superior chemical and UV resistance, making them ideal for surfaces exposed to vandalism and harsh cleaning agents.
Make Informed Choices
Choosing the right powder coating requires a clear understanding of the specific application requirements, including environmental exposure, durability needs, and chemical resistance. While this article provides a broad overview, consulting with your supplier is essential to ensure the optimal selection for your unique needs. By understanding the different powder coating chemistries and their applications, you can make more informed decisions and improve the longevity and performance of your coated products. For more information, please reach out to ecasebolt@chemquest.com
To learn more, reach out to the author at ecasebolt@chemquest.com or visit https://chemquest.com/cqpcr.
Read in ipcm.

